Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS): Why You Can’t Breathe Properly Through One Side of the Nose
Jump to your preferred language:
English
Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS): Why You Can’t Breathe Properly Through One Side of the Nose
Introduction
Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment options range from conservative management to surgical intervention, depending on severity.Feeling like one nostril is “always blocked” can be exhausting—especially at night, during exercise, or when you catch a cold. One of the most common structural reasons is a Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS), where the wall inside the nose (the septum) is not centered. At PRIME ENT Center Hardoi, Dr. Prateek Porwal and Dr. Harshita Singh regularly evaluate patients who have tried sprays and home remedies for years, only to discover that the real problem is mechanical—like a bent partition in the airway.At PRIME ENT Center Hardoi, we specialize in deviated nasal septum treatment options tailored to your specific condition severity.
This guide explains what DNS is, why it causes one-side blockage (and sometimes blockage on both sides), which symptoms should not be ignored, and what treatment options—including septoplasty—can realistically achieve.
First, a normal fact many people don’t know — the “nasal cycle”
Before blaming DNS, it helps to understand that mild alternating blockage can be normal.
- The nose has a natural rhythm called the nasal cycle where one side may feel more open while the other side feels slightly congested, and then they switch.
- This is usually more noticeable at night or when lying on one side.
Key difference: With DNS, the “blocked side” tends to be consistently worse and becomes much more uncomfortable during colds, allergies, or dusty exposure.
What is the nasal septum?
The nasal septum is the internal wall that divides the nose into right and left passages.
- The front part is mostly cartilage (more flexible).
- The back part is mostly bone (more rigid).
A straight septum helps air pass smoothly into the nose, allowing the nose to warm, humidify, and filter the air.
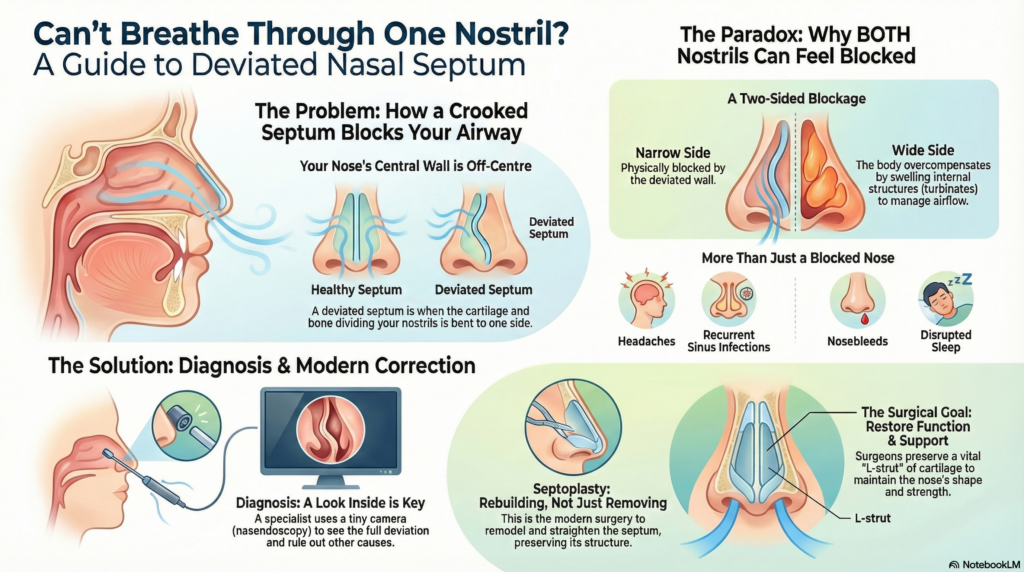
What is a Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)?
A DNS means the septum bends away from the midline, making one nasal passage narrower than the other.
Common patterns ENT specialists describe:
- C-shaped deviation: The septum curves mainly toward one side.
- S-shaped deviation: The septum curves one way in the front and the opposite way deeper inside.
- Septal spur: A sharp ridge/point at the cartilage-bone junction that can irritate the side wall.
- Caudal deviation/dislocation: The front-most part of the septum shifts, often causing severe blockage in one nostril.
Why you feel blocked — 3 mechanisms
1) Direct narrowing on the deviated side
The deviated septum physically reduces space, so air cannot pass freely.
- If the deviation is close to the internal nasal valve (the narrowest part of the nasal airway), even a small bend can feel dramatic.
2) “Paradoxical” blockage on the wider side
Many patients say: “Both sides feel blocked sometimes.” This can happen because the wider side often develops compensatory inferior turbinate hypertrophy.
- The turbinate (a structure that helps condition air) can enlarge to regulate airflow.
- The result: the “wide side” also starts feeling congested, especially during allergy season.
3) Secondary inflammation and drainage problems
A long-standing deviation can worsen nasal airflow patterns and contribute to:
- Rhinitis flare-ups (sensitivity, sneezing, watery nose).
- Sinus drainage blockage, which can trigger recurrent sinus pressure.
Symptoms of DNS (what patients commonly report)
At PRIME ENT Center Hardoi, the most frequent symptom is nasal obstruction, often worse on one side.
Other common symptoms include:These are the primary indicators of deviated nasal septum treatment being necessary:
- Mouth breathing, especially at night.
- Snoring or disturbed sleep.
- Frequent sinus pressure or facial heaviness.
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis), especially when a sharp spur dries and irritates the lining.
- Reduced smell (hyposmia), especially when swelling and obstruction coexist.
When DNS becomes more than “just blockage”
DNS itself is not an emergency, but certain patterns can seriously affect quality of life.If you experience significant Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment concerns, seeking evaluation is important.
Seek ENT evaluation sooner if you have:
- Blockage that affects sleep, exercise, or work performance.
- Recurrent sinus infections (or constant sinus pressure).
- Recurrent nosebleeds from one side.
- Headache/facial pain that seems linked to nasal blockage.
Urgent red flags (do not wait):
- Continuous heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop.
- Sudden swelling of the nose/face after injury.
- Severe headache with fever, swelling around eyes, or vision changes.
How ENT doctors diagnose DNS
A correct Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment diagnosis needs more than just “looking from outside.”
At PRIME ENT Center Hardoi, evaluation typically includes:
- History: When it started, which side is worse, effect of colds/allergies, snoring, headaches, and nosebleeds.
- Anterior rhinoscopy: A basic look inside the nose for obvious deviation, crusting, spur, and turbinate swelling.
- Nasal endoscopy: A thin camera to see deeper parts of the nose and the back of the septum.
- Decongestant test: If spray improves airflow a lot, swelling (allergy/rhinitis) contributes. If improvement is limited, the problem is likely structural.
- CT scan (only when needed): Mainly to assess sinus disease or complex anatomy before combined surgery.
Treatment options — what works and what doesn’t
1) Medical treatment (helps symptoms, doesn’t straighten the septum)
Medicines can help when DNS is mixed with swelling from allergy or infection.
- Saline nasal rinse to reduce dust/allergen load.
- Nasal steroid spray for allergic rhinitis (doctor-guided and regular use).
- Short-term decongestants only when advised (overuse can worsen congestion).
Important: No spray can permanently correct a bent septum.
2) Surgical treatment (definitive correction)
Septoplasty goals:
- Improve airflow by straightening/repositioning the septum.
- Preserve nasal support so the nose shape remains stable.
Some patients also require inferior turbinate reduction (when turbinate hypertrophy is significant) for best breathing results.
Septoplasty vs SMR (Submucosal Resection)
Both are septal surgeries, but the modern preference is usually septoplasty.
- Septoplasty: Conservative remodeling and repositioning of deviated parts, preserving structure.
- SMR: More extensive removal of deviated portions; used selectively depending on anatomy and surgeon preference.
Dr. Prateek Porwal explains it simply: septoplasty is like “straightening and reinforcing a bent wall,” while SMR is more like “removing larger bent parts,” which is why planning and technique matter.
What to expect after septoplasty (realistic recovery)
Every patient heals differently, but most people can expect:
- Day 1–2: Congestion, mild bleeding/oozing, pressure sensation.
- First week: Nasal blockage mainly from swelling/crusts (this is normal).
- 1–3 weeks: Steady improvement in breathing.
- 4–6 weeks: Most swelling settles; breathing feels much clearer.
Typical advice after surgery:
- Avoid nose blowing for a few days (follow your surgeon’s plan).
- Do saline rinses as prescribed.
- Avoid heavy gym and bending for 1–2 weeks.
- Return for follow-ups for cleaning and monitoring.
DNS and sinusitis — what’s the connection?
Many patients with DNS also complain of “sinus” headaches or facial heaviness. DNS may contribute by:
- Creating airflow turbulence and dryness, which irritates the nasal lining.
- Narrowing the area where sinuses drain (different people have different sinus anatomy), so mucus may stagnate.
It is important to understand that DNS is not the only cause of sinusitis. Allergic rhinitis, pollutants, and infections can also trigger sinus problems. That’s why evaluation must look at the whole nose, not just the septum.
DNS and ear symptoms — can the nose affect the ear?
Some patients notice ear fullness, popping, or mild hearing fluctuation along with nasal blockage.
- The nose and ear are connected through the Eustachian tube, and chronic nasal congestion can worsen Eustachian tube function.
- This doesn’t mean DNS directly “causes ear infection,” but a blocked, inflamed nose can make ear pressure regulation harder.
Home care that actually helps (safe, practical habits)
While home care can’t straighten the septum, it can reduce swelling and improve comfort—especially in people who have both Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment needs and rhinitis.
- Saline rinse once or twice daily (as advised): helps wash out dust/pollen and reduces crusting.
- Steam inhalation: may temporarily soothe dryness, but don’t expect it to correct structural blockage.
- Sleep position: many people breathe slightly better if they sleep with the head elevated and avoid very dusty bedding.
- Hydration: dryness worsens crusting and nosebleeds.
Avoid: self-prescribed prolonged decongestant sprays (these can cause rebound congestion in many people).
Septoplasty — step-by-step (what happens in the OT)
A typical septoplasty plan includes:
- Pre-op evaluation: symptom assessment, nasal exam, and endoscopy; CT only if needed.
- Anesthesia: usually general anesthesia for comfort and precision.
- Internal incision: the cut is made inside the nose (no visible scar in most cases).
- Mucosal elevation: the lining is lifted carefully to expose cartilage/bone.
- Correction: deviated portions are reshaped, repositioned, or selectively removed while preserving support.
- Stabilization: the septum is supported (often with sutures and/or silicone splints depending on case).
- Packing (sometimes): some surgeons use light packing for a short period to control bleeding.
Dr. Harshita Singh emphasizes an important point: the best results come from matching the technique to the deviation type—especially for caudal deviations and sharp spurs.
Possible risks and complications (transparent and practical)
Possible issues include:
- Bleeding and temporary oozing.
- Septal hematoma (collection of blood): rare but needs urgent treatment to protect cartilage.
- Infection (uncommon with proper care).
- Septal perforation (a hole in the septum): rare; can cause whistling or crusting.
- Residual deviation / persistent blockage: sometimes due to turbinate swelling, nasal valve issues, or complex deviation.
A good ENT plan checks for coexisting causes of blockage such as allergic rhinitis, turbinate hypertrophy, or nasal valve weakness.
Myth vs fact (quick clarity)
- Myth: “DNS always needs surgery.”
- Fact: DNS needs surgery only when symptoms are significant and persistent.
- Myth: “Septoplasty is cosmetic surgery.”
- Fact: Septoplasty is functional surgery to improve breathing.
- Myth: “If sprays help a little, DNS is not present.”
- Fact: DNS can exist along with swelling; sprays may reduce swelling but cannot correct the bend.
A simple self-check before your appointment
This doesn’t replace diagnosis, but it helps you describe symptoms clearly:
- Which side is usually worse? Right, left, or alternates?
- Is it worse at night, during exercise, or during colds?
- Do you snore or wake with dry mouth?
- Any recurrent nosebleeds, facial pain, or reduced smell?
FAQs (Parents & patients ask these often)
Q1. If I can breathe from one side sometimes, do I still have DNS?
Yes, Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment can still be necessary even if you can breathe from one side sometimes. Swelling changes daily, so symptoms fluctuate, but the structural narrowness remains.
Q2. Can DNS cause headaches?
It can contribute—either due to sinus drainage issues or contact/pressure from a spur in select cases.
Q3. Will septoplasty change my nose shape?
Septoplasty is designed to improve internal airflow and usually does not change the external shape. If cosmetic changes are needed, that is a separate discussion.
Q4. Is septoplasty safe?
When done by trained ENT surgeons with proper evaluation, it is a commonly performed procedure. Like all surgeries, it has risks (bleeding, infection, septal hematoma, perforation), which are discussed during consent.
Q5. When should I meet an ENT specialist?
If one-side blockage is persistent for weeks, disrupts sleep, causes repeated sinus infections, or is associated with frequent nosebleeds, evaluation for Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) treatment options is recommended.
For evaluation, consult Dr. Prateek Porwal or Dr. Harshita Singh.
Hinglish
DNS (Deviated Nasal Septum): Ek Side Se Saans Kyun Nahi Aati?
Introduction
Agar aapko lagta hai ki naak ka ek side hamesha band rehta hai—ya sone ke time saans lene mein dikkat hoti hai—toh iski ek common wajah Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) ho sakti hai. PRIME ENT Center Hardoi mein Dr. Prateek Porwal aur Dr. Harshita Singh bohot saare patients ko dekhte hain jinhone saalon tak sprays try kiye, lekin relief isliye nahi mila kyunki problem “inside structure” mein thi.
Is Hinglish guide mein hum simple language mein samjhenge:
- DNS kya hota hai
- Ek side blockage kyun hota hai
- Kab medicines help karti hain
- Kab septoplasty ka option consider karna chahiye
Pehle ye samjho — Nasal Cycle normal hota hai
Kabhi-kabhi ek side band aur doosra side khula feel hona normal hai.
- Isse nasal cycle bolte hain.
- Lekin DNS mein ek side consistently zyada band feel hota hai.
DNS kya hota hai?
Naak ke andar ek deewar hoti hai jise nasal septum kehte hain. Agar ye deewar seedhi na ho aur ek side jhuk jaye, toh usse DNS kehte hain.
DNS ke common types:
- C-shaped / S-shaped
- Septal spur (tez kona)
- Caudal deviation (front mein zyada jhukav)
Ek side blockage kyun hota hai? (3 reasons)
1) Narrow side par direct blockage
Jis side septum jhukta hai, us side space kam ho jata hai.
2) Wide side par turbinate ka swell hona
Opposite side (jo wide hota hai) wahan inferior turbinate swell ho sakta hai. Isse aapko lagta hai ki “dono side band” ho rahe.
3) Allergy/sinus ka effect
DNS ke saath agar allergy ya sinusitis bhi ho, toh blockage double feel hota hai.
DNS ke symptoms (patients ki language mein)
- Ek side se saans nahi aana
- Raat ko mouth breathing
- Snoring
- Recurrent sinus pressure
- Nosebleed (khaaskar agar spur ho)
- Smell kam hona
PRIME ENT Center Hardoi mein diagnosis kaise hota hai?
Dr. Harshita Singh normally:
- Nose check (anterior rhinoscopy)
- Nasal endoscopy (camera se inside)
- Kabhi-kabhi CT scan (agar sinus issue suspect ho)
Ek simple clue: decongestant spray se agar relief aa gaya, toh swelling (allergy) major factor ho sakti hai. Agar relief nahi aaya, toh structural DNS strong possibility hoti hai.
Treatment — Medicine vs Surgery
Medicine kab help karegi?
- Saline rinse
- Allergy spray (doctor advice)
- Short course decongestant (sirf advice par)
Important: Medicine septum ko seedha nahi kar sakti.
Septoplasty kab consider karein?
Dr. Prateek Porwal usually tab suggest karte hain jab:
- Blockage daily life aur sleep disturb kare
- Recurrent sinus infections ho
- Continuous one-side obstruction ho
Kabhi-kabhi turbinate reduction bhi saath mein karna padta hai, taaki breathing properly improve ho.
Septoplasty ke baad recovery (simple timeline)
- Pehle 2 din: congestion + mild oozing normal
- 1 week: swelling/crusts ki wajah se band feel hoga
- 2–3 week: breathing noticeably better
- 4–6 week: best improvement feel hota hai
DNS aur sinus ka connection
Kai log bolte hain: “Mujhe sinus headache hota hai.” DNS kuch cases mein sinus drainage ko affect karke pressure badha sakta hai.
- Lekin yaad rakhein: sinus ka reason sirf DNS nahi hota; allergy aur infection bhi major reasons hote hain.
Ghar par kya karein? (Safe habits)
DNS ko ghar par seedha nahi kiya ja sakta, but symptoms ko control kiya ja sakta hai:
- Saline rinse – crusting/dust kam hota hai.
- Steam – temporary comfort mil sakta hai.
- Head elevation – sone ke time pillow thoda ucha rakhein.
Avoid: bina doctor ke decongestant spray ko lambi duration tak use karna.
Septoplasty ka process (simple)
1) Naak ke andar se incision
2) Septum ki lining ko gently lift
3) Tedha cartilage/bone ko straighten/reposition
4) Silicone splints/packing (case ke hisab se)
5) Follow-up cleaning
Myth vs Fact
- Myth: “DNS ka spray se permanent ilaaj ho jata hai.”
- Fact: Spray swelling kam karta hai, septum ko seedha nahi karta.
- Myth: “Septoplasty bahut risky hota hai.”
- Fact: Proper evaluation aur trained surgeon ke saath ye common procedure hai.
FAQs
Q: Kya septoplasty cosmetic surgery hai?
Nahi, septoplasty functional surgery hai—breathing improve karne ke liye.
Q: Kya DNS headache de sakta hai?
Haan, kuch cases mein sinus pressure ya spur contact ki wajah se.
Q: Kab turant doctor ko dikhana chahiye?
Agar heavy nosebleed ruk nahi raha, injury ke baad swelling, ya fever ke saath severe headache ho.
Appointment ke liye Dr. Prateek Porwal ya Dr. Harshita Singh se consult karein.
हिंदी
Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS): नाक के एक तरफ से साँस क्यों नहीं आती?
बहुत से लोगों को लगता है कि “नाक का एक साइड हमेशा बंद रहता है” और पूरी साँस नहीं आ पाती। कई बार यह Allergy या Cold की वजह से होता है, लेकिन एक बहुत सामान्य structural कारण है Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)। PRIME ENT Center Hardoi में Dr. Prateek Porwal और Dr. Harshita Singh ऐसे मरीजों की नियमित जाँच करते हैं जिनको सालों से एक तरफ़ की blockage रहती है—और spray से स्थायी फायदा नहीं मिलता।
इस लेख में आप जानेंगे कि DNS क्या होता है, इसके लक्षण क्या हैं, और कब Septoplasty की जरूरत पड़ सकती है।
Nasal Septum क्या है?
नाक के अंदर एक दीवार होती है जो नाक को दाएँ और बाएँ दो हिस्सों में बाँटती है। इसे nasal septum कहते हैं। इसका आगे का भाग cartilage और पीछे का भाग bone से बना होता है।
DNS (Deviated Septum) क्या होता है?
जब septum बीच की लाइन से हटकर एक तरफ झुक जाता है, तो उस तरफ हवा का रास्ता कम हो जाता है।
DNS के कुछ common रूप:
- C-shaped deviation
- S-shaped deviation
- Septal spur (नुकीला उभार)
- Caudal deviation (अगले हिस्से में ज्यादा टेढ़ापन)
एक तरफ blockage क्यों होता है?
1) जिस तरफ septum झुका है, उस तरफ रास्ता narrow हो जाता है।
2) दूसरी तरफ (जो initially open होती है), वहाँ inferior turbinate hypertrophy हो सकता है, जिससे “दूसरी तरफ भी बंद” महसूस हो सकता है।
3) DNS के साथ अगर rhinitis/sinusitis भी हो, तो blockage बढ़ जाता है।
DNS के लक्षण (Symptoms)
- एक तरफ से साँस न आना (unilateral nasal obstruction)
- रात में मुँह से साँस लेना (mouth breathing)
- Snoring और sleep disturbance
- बार-बार sinus pressure या facial heaviness
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- smell कम होना (hyposmia)
Diagnosis (जाँच) कैसे होती है?
Dr. Harshita Singh आमतौर पर:
- Anterior rhinoscopy से नाक के अंदर देखती हैं
- जरूरत पर Nasal endoscopy करती हैं
- अगर sinus problem suspect हो, तो CT scan की सलाह दी जा सकती है
एक practical point: decongestant spray से अगर blockage काफी कम हो जाए, तो swelling/allergy factor हो सकता है। अगर नहीं सुधरे, तो DNS structural issue strong होता है।
Treatment (इलाज)
1) Medical management
- Saline rinse
- Allergic rhinitis के लिए nasal steroid spray (doctor guidance)
- Short-term decongestant (self-use से बचें)
लेकिन: दवाइयाँ septum को सीधा नहीं कर सकतीं।
2) Surgical management — Septoplasty
जब blockage लगातार बना रहे और lifestyle/sleep पर असर डाल रहा हो, तब Septoplasty definitive treatment है।
- इसमें septum के टेढ़े हिस्से को remodel/reposition करके airway open किया जाता है।
- कुछ मरीजों में turbinate reduction भी साथ में करनी पड़ सकती है।
Surgery के बाद care
- शुरुआती 1–2 दिन congestion और हल्का bleeding/oozing normal हो सकता है
- 1 हफ्ते तक swelling की वजह से band feel हो सकता है
- 2–3 हफ्तों में breathing improve होने लगता है
- 4–6 हफ्तों में काफी अच्छा comfort आता है
DNS और Sinusitis का संबंध
कई मरीज कहते हैं कि उन्हें “Sinus headache” या चेहरे में दबाव (facial pressure) रहता है। DNS कुछ मामलों में नाक के airflow और sinus drainage pathway को प्रभावित कर सकता है, जिससे परेशानी बढ़ सकती है।
लेकिन यह भी सच है कि sinusitis के कारण केवल DNS नहीं होते—Allergy, infection, और pollution भी कारण हो सकते हैं। इसलिए सही जाँच जरूरी है।
घर पर क्या करें? (Safe care)
DNS को घर पर सीधा नहीं किया जा सकता, लेकिन swelling और dryness कम की जा सकती है:
- Saline nasal rinse (डॉक्टर की सलाह अनुसार)
- पर्याप्त पानी पीना (hydration)
- धूल/धुआँ से बचना
- रात में सिर थोड़ा ऊँचा रखकर सोना
ध्यान दें: बिना सलाह के decongestant spray लंबे समय तक न लें।
Septoplasty कैसे होती है? (सरल समझ)
- ऑपरेशन आमतौर पर नाक के अंदर से किया जाता है, इसलिए बाहर कोई बड़ा निशान नहीं होता।
- Septum की lining को सावधानी से उठाकर टेढ़े हिस्से को straight/reposition किया जाता है।
- कुछ केस में silicone splints या हल्की packing लगाई जा सकती है।
Myth vs Fact
- Myth: “Spray से DNS हमेशा ठीक हो जाता है।”
- Fact: Spray केवल swelling कम कर सकता है; DNS structural है।
- Myth: “Septoplasty cosmetic surgery है।”
- Fact: Septoplasty functional surgery है जिसका लक्ष्य breathing improve करना है।
FAQs
Q: Septoplasty से nose का shape बदलता है?
Septoplasty functional surgery है; external shape change सामान्यतः नहीं होता।
Q: क्या DNS से headache हो सकता है?
कुछ cases में sinus drainage issues या spur contact की वजह से pain हो सकता है।
Appointment के लिए Dr. Prateek Porwal या Dr. Harshita Singh से consult करें।

